Table Of Content
Exploring Skin Pigmentation: Causes, Types, and Treatment Options
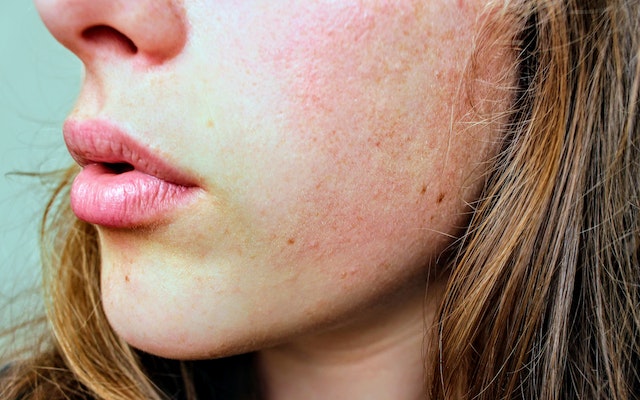
Skin pigmentation is the color of the skin, which is caused by melanin that is made by special cells. Melanin is the color made by melanocytes, which are special skin cells. Melanin gives the skin, mucous tissues, and retina of the eye different shades of color. People with fair and mature skin have less melanin in their bodies than people with dark skin.
People's skin color and melanin are changed by their genes, how much UV light they get, and some drugs.
Many skin diseases that cause pigmentary abnormalities can change how a person looks and how well they get along with others. Melasma, Vitiligo, Albinism, and Addison's disease are all common skin pigmentation problems. Eczema, acne vulgaris, and drug interactions can all cause them. Today, we talked about what causes skin color, what kinds there are, and how to treat them.
Causes Of Skin Pigmentation
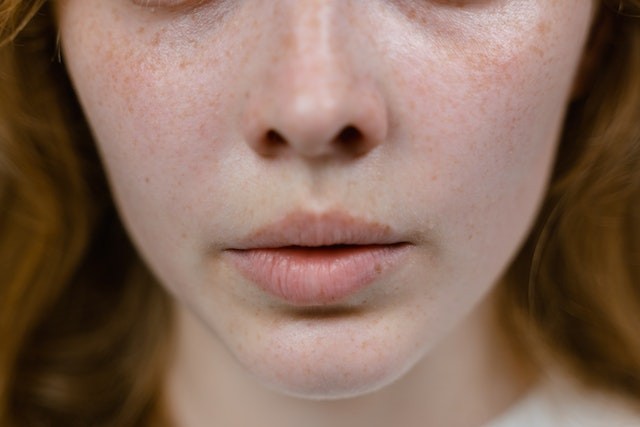

Melanocytes:
Melanocytes are special cells in the outer layer of your skin that make melanin. Melanosomes are small parts inside the cells that make melanin. The different colors of skin rely on how well these tiny melanin factories work. Below, we talk about the two main types of melanin:
Eumelanin:
It keeps your skin safe and is brown and black. The small amount of harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays that get through the oxygen radicals could hurt your cells and lead to long-term health problems like cancer.
Pheomelanin:
Its colors are red and yellow. Pheomelanin protects a little bit against dangerous ultraviolet (UV) rays and helps make oxygen radicals, which do damage.
Both internal and exterior factors can cause the body to make more melanin, which can cause skin pigmentation problems. You can talk to a doctor to find out what the exact cause is.
Some of the common factors that cause skin pigmentation are given below:
External Factors
- Injury: A cut, bruise, or depilatory cream can cause an inflammatory reaction at the spot of a skin injury. Because of this, the body makes more melanin, which makes the skin darker.
- Medication: Chemotherapy uses skin pigmentation caused by side effects of medicines like tetracycline drugs.
- Exposure to the sun: Ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B (UVB) rays are coming to us from the sun. UVA rays cause more melanin to be made, which makes the skin darker.
Internal Factors
- Heredity factors: Hereditary factors are the most important cause of face color. For example, damaging sun rays can cause Lentigines, which are dark spots on parts of the body. Lentigines are linked to multi-systemic syndromes.
- Hormonal changes: The amount of estrogen and progesterone in the body goes up, which causes melasma, or dark spots on the skin. Changes in hormones could be caused by pregnancy.
- Disease: Addison's disease changes the amount of hormones in the body, which causes melanin to be made and darkens the skin.
Types Of Skin Pigmentation
Skin damage and other changes in the body can make the skin darker or change its color. This can happen in more than one place on the body's surface. There are three different kinds of skin color:
Hyperpigmentation
In hyperpigmentation, skin becomes darker than the surrounding areas. It may occur in small patches of the skin and may affect the whole body as well. Types of hyperpigmentation are;
- Melasma: Melasma is uncontrolled production of melanin pigmentation on the skin, it may be caused due to pregnancy. The cause of melasma is exposure to the sun.
- Freckles: Freckles are the commonly occurring type of pigmentation. Genetics plays a main role in producing little spots on the skin. Repeatedly exposure to the sun and prevalent in individuals with a fairer complexion is also a major reason.
Hypopigmentation
Hypopigmentation is when your body makes less melanin, which makes your skin lose its color. Because it has less melanin than discoloration, it is lighter in color. It can also be caused by sickness. Hypopigmentation can look like:
- Albinism: It happens when there is no melanin at all, so the face, hair, and eyes are all the same color. Albinism can't be cured by drugs, which is a shame.
- Pityriasis: Pityriasis is a skin condition that causes dark spots on the skin that are slightly raised. It might be linked to dry skin.
Depigmentation
Depigmentation is when your skin loses its color and goes white. Vitiligo is a common autoimmune disease that causes patches of skin to lose their color and look smooth and white.
Treatments for Skin Pigmentation
For an accurate diagnosis, you should seek help from an experienced dermatologist. The doctor recommends the treatment depending on the types of pigmentation.
- Examining the skin
- Derma scan analysis or asking about the medical history
- Taking a biopsy helps to rule out skin cancer
- Asking about sun exposure
- Topical cream
- Chemical peels
- Laser resurfacing
- Microdermabrasion
- Intense pulse light (IPL)
Conclusion
The term "pigmentation of the skin" comes from the fact that it is used to describe the color of the skin, which in turn reveals the amount of melanin that is produced by melanocytes. Sun exposure, hereditary factors, and hormonal shifts are the primary contributors to the development of skin pigmentation. We hope this blog may be helpful to you.
Author






Top 10 Travеling Tips for Pеt Ownеrs
Best Body Washes For Dry Skin Under $50
8 Best Moisturizers for Mature Skin
How to Curl Your Hair to Make Your Style Last
Barbie Tattoo Ideas for the Doll-Loving Ink Enthusiasts
Selena Gomez and Hailey Bieber Drama Takеs thе Spotlight In Entеrtainmеnt Nеws
Michael Kors Shoes: The Perfect Addition to Your Shoe Collection
Lululemon Yoga Mats: Which One Is Best for You?